The term “Memoization” comes from the Latin word “memorandum” (to remember), which is commonly shortened to “memo” in American English, and which means “to transform the results of a function into something to remember.”.
In computing, memoization is used to speed up computer programs by eliminating the repetitive computation of results, and by avoiding repeated calls to functions that process the same input.
What is memoization
Why is Memoization used?
Memoization is a specific form of caching that is used in dynamic programming. The purpose of caching is to improve the performance of our programs and keep data accessible that can be used later. It basically stores the previously calculated result of the subproblem and uses the stored result for the same subproblem. This removes the extra effort to calculate again and again for the same problem. And we already know that if the same problem occurs again and again, then that problem is recursive in nature.
Where to use Memoization?
We can use the memoization technique where the use of the previously-calculated results comes into the picture. This kind of problem is mostly used in the context of recursion, especially with problems that involve overlapping subproblems.
Let’s take an example where the same subproblem repeats again and again.
Example to show where to use memoization:
Let us try to find the factorial of a number.
Below is a recursive method for finding the factorial of a number:
int factorial(unsigned int n)
{
if (n == 0)
return 1;
return n * factorial(n – 1);
}
What happens if we use this recursive method?
If you write the complete code for the above snippet, you will notice that there will be 2 methods in the code:
1. factorial(n) 2. main()
Now if we have multiple queries to find the factorial, such as finding factorial of 2, 3, 9, and 5, then we will need to call the factorial() method 4 times:
factorial(2) factorial(3) factorial(9) factorial(5)
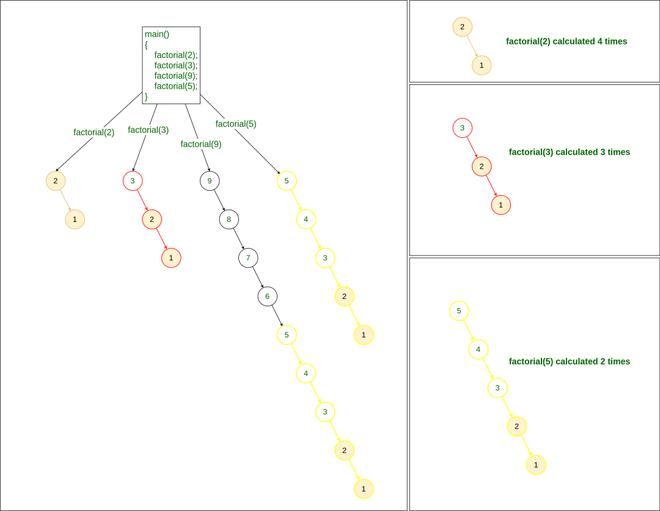
Recursive method to find Factorial
So it is safe to say that for finding factorial of numbers K numbers, the time complexity needed will be O(N*K)
- O(N) to find the factorial of a particular number, and
- O(K) to call the factorial() method K different times.
How Memorization can help with such problems?
If we notice in the above problem, while calculation factorial of 9:
- We are calculating the factorial of 2
- We are also calculating the factorial of 3,
- and We are calculating the factorial of 5 as well
Therefore if we store the result of each individual factorial at the first time of calculation, we can easily return the factorial of any required number in just O(1) time. This process is known as Memoization.
Solution using Memoization (How does memoization work?):
If we find the factorial of 9 first and store the results of individual sub-problems, we can easily print the factorial of each input in O(1).
Therefore the time complexity to find factorial numbers using memorization will be O(N)
- O(N) to find the factorial of the largest input
- O(1) to print the factorial of each input.
Types of Memoization
The Implementation of memoization depends upon the changing parameters that are responsible for solving the problem. There are various dimensions of caching that are used in memoization technique, Below are some of them:
- 1D Memoization: The recursive function that has only one argument whose value was not constant after every function call.
- 2D Memoization: The recursive function that has only two arguments whose value was not constant after every function call.
- 3D Memoization: The recursive function that has only three arguments whose values were not constant after every function call.
How Memoization technique is used in Dynamic Programming?
Dynamic programming helps to efficiently solve problems that have overlapping subproblems and optimal substructure properties. The idea behind dynamic programming is to break the problem into smaller sub-problems and save the result for future use, thus eliminating the need to compute the result repeatedly.
There are two approaches to formulate a dynamic programming solution:
- Top-Down Approach: This approach follows the memoization technique. It consists of recursion and caching. In computation, recursion represents the process of calling functions repeatedly, whereas cache refers to the process of storing intermediate results.
- Bottom-Up Approach: This approach uses the tabulation technique to implement the dynamic programming solution. It addresses the same problems as before, but without recursion. In this approach, iteration replaces recursion. Hence, there is no stack overflow error or overhead of recursive procedures.
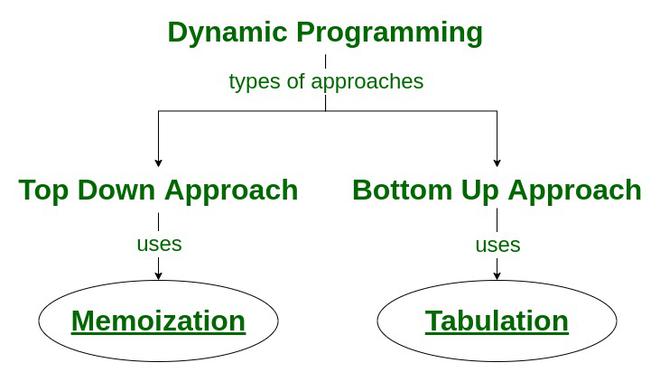
How Memoization technique is used in Dynamic Programming
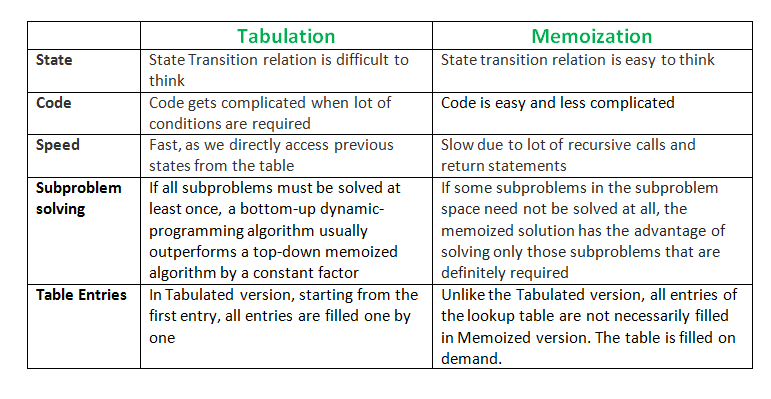
How Memoization is different from Tabulation?
For more details please refer: Tabulation vs. Memoization
Coding Practice Problems on Memoization
| Question | Article | Practice | Video |
|---|---|---|---|
| Count ways to reach the n’th stair | View | Solve | Watch |
| Word Break Problem | DP-32 | View | Solve | Watch |
| Program for Fibonacci numbers | View | Solve | Watch |
| nth Catalan Number | View | Solve | Watch |
| Gold Mine Problem | View | Solve | Watch |
| Subset Sum Problem | View | Solve | Watch |
| Cutting a Rod | View | Solve | Watch |
| Min Cost Path | View | Solve | Watch |
| Minimum number of jumps to reach end | View | Solve | Watch |
| Longest Palindromic Substring | Set 1 | View | Solve | Watch |
| Longest Repeating Subsequence | View | Solve | Watch |
| Count ways to reach the nth stair using step 1, 2 or 3 | View | Solve | Watch |
| Count of different ways to express N as the sum of 1, 3 and 4 | View | Solve | Watch |
| Count number of ways to cover a distance | View | Solve | Watch |
| Count of arrays having consecutive element with different values | View | Solve | Watch |
| Largest Sum Contiguous Subarray | View | Solve | Watch |
| Smallest sum contiguous subarray | View | Solve | Watch |
| Unique paths in a Grid with Obstacles | View | Solve | Watch |
| Different ways to sum n using numbers greater than or equal to m | View | Solve | Watch |
Frequently asked questions (FAQs) about Memoization
1: Is memoization better than DP?
Memoization is the top-down approach to solving a problem with dynamic programming. It’s called memoization because we will create a memo for the values returned from solving each problem.
2: Is memoization the same as caching?
Memoization is actually a specific type of caching. The term caching can generally refer to any storing technique (like HTTP caching) for future use, but memoizing refers more specifically to caching function that returns the value.
3: Why memoization is top-down?
The top-Down approach breaks the large problem into multiple subproblems. if the subproblem is solved already then reuse the answer. Otherwise, Solve the subproblem and store the result in some memory.
4: Does memoization use recursion?
Memoization follows top-down approach to solving the problem. It consists of recursion and caching. In computation, recursion represents the process of calling functions repeatedly, whereas cache refers to the process of storing intermediate results.
5: Should I use tabulation or memoization?
For problems requiring all subproblems to be solved, tabulation typically outperforms memoization by a constant factor. This is because the tabulation has no overhead of recursion which reduces the time for resolving the recursion call stack from the stack memory.
Whenever a subproblem needs to be solved for the original problem to be solved, memoization is preferable since a subproblem is solved lazily, i.e. only the computations that are required are carried out.
6: Where is memoization used?
Memoization is an optimization technique used to speed up computer programs by caching the results of expensive function calls and returning them when the same inputs are encountered again.
7: Why is it called memoization?
The term “memoization” comes from the Latin word “memorandum” (“to remember”), which is commonly shortened to “memo” in American English, and which means “to transform the results of a function into something to remember.”.
8: How does memoization reduce time complexity?
Solving the same problem again and again takes time and increases the run-time complexity of the overall program. This problem can be resolved by maintaining some cache or memory where we will store the already calculated result of the problem for some particular input. So that if we don’t want to recalculate the same problem, we can simply use the result that is stored in the memory and reduce the time complexity.
9: What is the difference between memoization and caching?
Memoization is actually a specific type of caching that involves caching the return value of a function based on input. Caching is a more general term. For example, HTTP caching is caching but it is not memoization.
10: Why tabulation is faster than memoization?
Tabulation is usually faster than memoization, because it is iterative and solving subproblems requires no overhead of recursive calls.
Conclusion
Memoization is a programming concept and can be applied to any programming language. Its absolute goal is to optimize the program. Usually, this problem is seen when programs perform heavy computations. This technique cache all the previous result that is computed so that it will not have to recalculate for the same problem.
Related Articles: