We are thrilled to announce the launch of the Generative AI 2024 report, a comprehensive analysis of the latest trends, tools, benefits, and challenges in the generative artificial intelligence field.
Sponsored by WEKA, this report provides an in-depth look at how AI practitioners and end users navigate the landscape of generative AI tools, offering valuable insights into their preferences, priorities, and pain points.
In this preview, we present key findings from Section 8 of the report, focusing on the main generative AI tools of choice, their perceived benefits, and the challenges faced by users. This snapshot highlights significant shifts from last year, revealing emerging trends and changing attitudes towards these transformative technologies.
Download the complete Generative AI 2024 Report to delve deeper into these insights and explore the full breadth of data and analysis.
Main generative AI tool of choice, benefits, and challenges
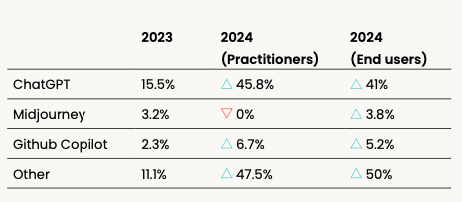
Not only does ChatGPT continue to be the main tool of choice compared to last year (15.5%), but it also had a higher percentage of use among both practitioners (47.5%) and end users (41%).
Copilot was mentioned more frequently this year; however, in spite of ChatGPT still leading the generative AI tool choice, we saw a much wider variety of tools mentioned than in 2023.
Among practitioners, we saw the following tools:

Among end users, we saw the following tools:

What is the main benefit of your number one choice?
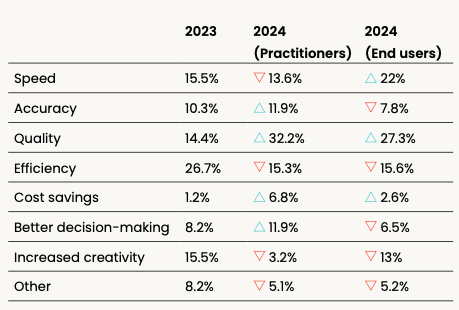
In 2023, efficiency (26.7%) was ruled as the main benefit of respondents’ number one tool of choice.
This year, we saw a shift in priorities, with practitioners (32.2%) and end users (27.3%) agreeing that quality is now more important. Users are looking for tools that can effectively perform their tasks while being extremely accurate and reliable. This switch could be due to generative AI tools being increasingly used for vital business functions, and errors in these situations can be costly.
Efficiency was still the second most important reason for practitioners (15.3%), while end users highlighted speed (22%) instead.
This difference highlights how practitioners and end users have varied requirements; the former can often work with complex and multifaceted tasks that need tools to maximize resources while keeping waste to a minimum, while the latter might prioritize how quickly a tool can deliver what they need according to everyday tasks.
What is the main challenge of your number one choice?
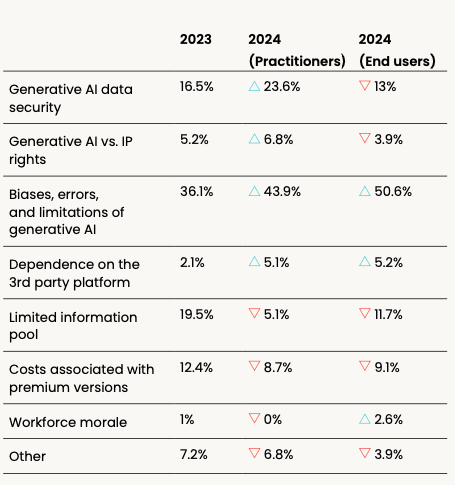
For the second year in a row, biases, errors, and limitations of generative AI are considered to be the main challenge of the number one tool of choice.
This is more important for end users (50.6%) than for practitioners (43.9%), who equally value generative AI data security in second place with 13% and 23.6%, respectively.
Perhaps surprisingly, this represents a change from last year when generative AI technology was newer. In 2023, the limited information pool was the second biggest challenge, with generative AI data security falling after.
This could point to a general increase in awareness about the tools and their capabilities, especially with higher discussions behind the ethics and governance of generative AI.
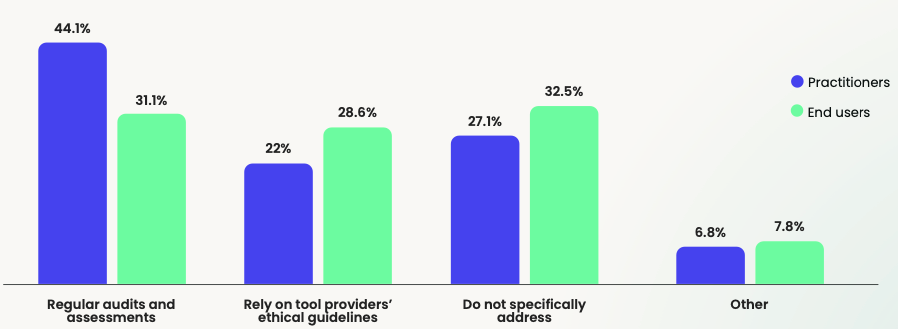
As previously mentioned, the ethics behind generative AI can be a concern, and this year, we wanted to know how respondents are addressing these considerations as they continue to use the tools.
The plurality of practitioners (44.1%) highlighted regular audits and assessments as the main way to address ethical challenges. Suggesting a structured and proactive approach within this community, regular audits often lead to the identification and mitigation of potential issues for transparency with stakeholders and compliance with ethical norms or regulations.
This, however, was a very close second for end users (31.1%), who mainly reported that they didn’t specifically address any ethical concerns (32.5%). This could indicate the existence of a slight gap in awareness or resources to address issues, and end users might be less equipped to fully delve into the ethical considerations of generative AI tools.
Curious to know more insights about generative AI in 2024? Don’t miss out – download your FREE copy of the report today!

