Routing is the process of selecting a path along which the data can be transferred from the source to the destination. In this article, we will see default routing and its configuration in the cisco packet tracer.
It is a type of routing which is useful in those cases when the destination network id is unknown to the router. In such cases, the router will use a default route and will send all the incoming traffic to that route, by default. Generally used on the internet where the destinations are unknown. Default Routing is a method wherein a router is configured to ship all of the packets to the equal hop tool, and it would not be counted whether or not it belongs to a specific community or not. a packet is transmitted to the tool for which it’s far configured in default routing.
- We can say that default routing can be considered a special type of static routing.
- The default route is used to send data packets to an unknown target to a single next-hop address.
For more details please refer Types of Routing article.
Default Routing is used while networks address a single go-out point. It is also useful while the bulk of transmission networks need to transmit the information to the equal hop device.
When a particular route is referred to withinside the routing table, the router will pick the particular route as opposed to the default route. The default route is selected most effective whilst a particular route is not referred to in the routing table.
Example: The Address of Yahoo is unknown.
- It is the last preferred routing
- Also can be used at end locations.
- Default routes help in reducing the size of your routing table.
CLI command: R-1(config)#ip route (any destination) (any subnet mask) (next hop IP address) R-1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.2
Steps to Configure the Default Routing in Cisco packet Tracer:
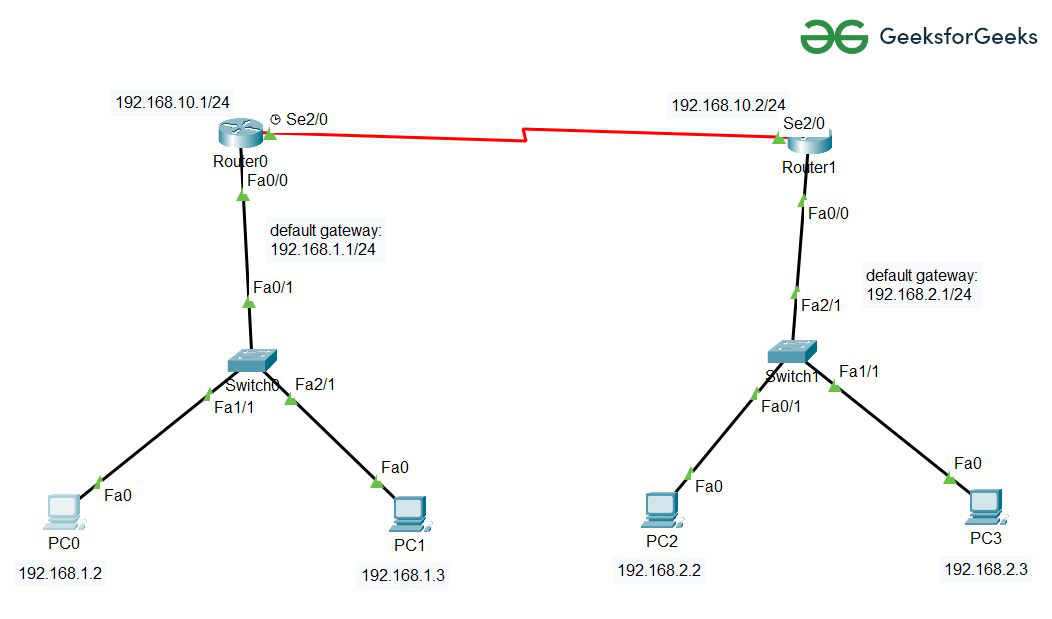
Step 1: First, create a network topology of these given devices listed below in the table:
| S.No | Device | Model name | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | PC | pc | 4 |
| 2. | Switch | PT-switch | 2 |
| 3. | Router | PT-Router | 2 |
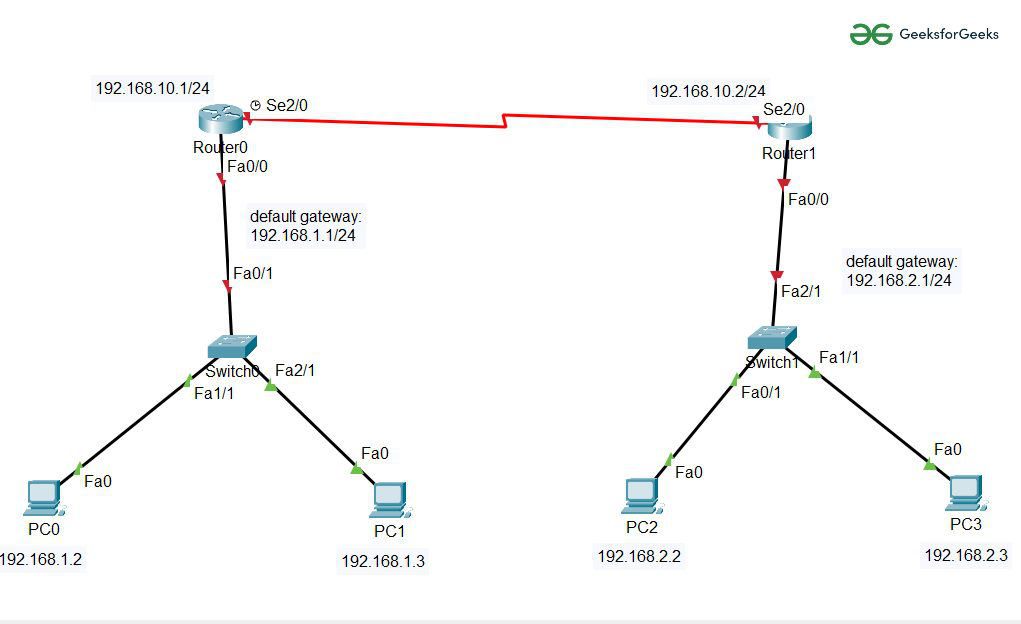
Step 2: Configuring Hosts (PCs) with IP addresses and Default Gateway using IP Addressing table given below:
| Device name | IPv4 Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|
| PC0 | 192.168.1.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 |
| PC1 | 192.168.1.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 |
| PC2 | 192.168.2.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.2.1 |
| PC3 | 192.168.2.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.2.1 |
To configure PCs follow these steps:
- Click on PC0 then go to desktop.
- Click on IP configuration.
- Then on the static route, fill up the IP configuration according to the IP addressing table given above.
- Repeat the same procedure with other PCs to configure them.
Step 3: Configuring the Interfaces (routers) with IP Addresses and Default gateways and assigning the default routes.
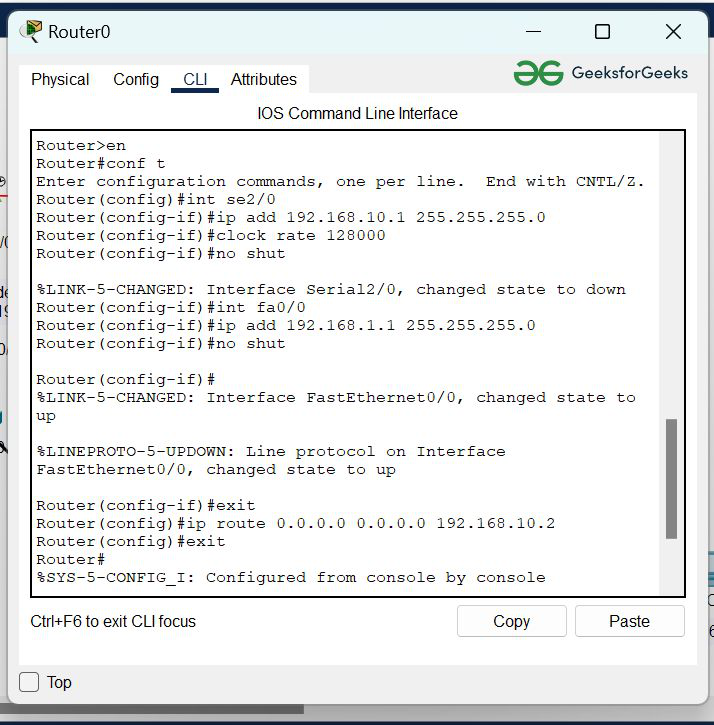
Router0 Configuration:
- Click on router0 then, Go to CLI commands and enter commands to configure them given below.
- Now we will add the IP address of the serial se2/0 and its subnet mask.
- In this step, we will add the IP address of the interface FastEthernet port fa0/0 and its subnet mask.
- Then we need to add Default Routes to configure the router:
R-1(config)#ip route (any destination~reserved) (any subnet mask~reserved) (next hop IP address)
- Add the IP address of the next hope to connect with another LAN.
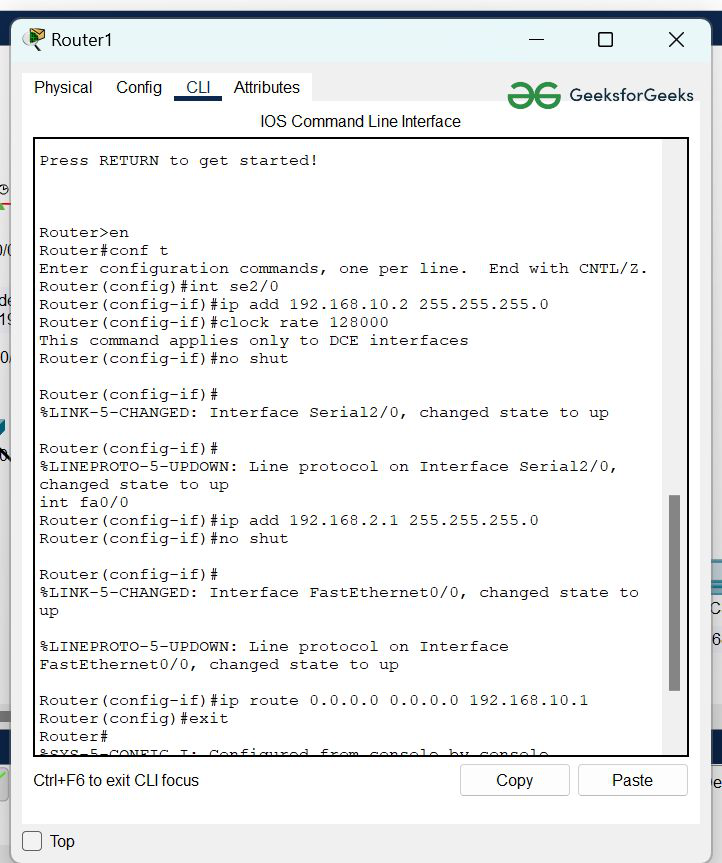
Router1 Configuration:
- Click on the router1 then, Go to CLI commands, and enter commands to configure them given below.
- Now, we will add the IP address of the serial se2/0 and its subnet mask.
- Second, we will add the IP address of the interface FastEthernet port fa0/0 and its subnet mask.
- Then we need to add Default Routes to configure the router:
R-1(config)#ip route (any destination~reserved) (any subnet mask~reserved) (next hop IP address)
- Add the IP address of the next hope to connect with another LAN.
Step 4: After configuring all the devices red indicator turns into green and the network is live so we can send and receive packets.
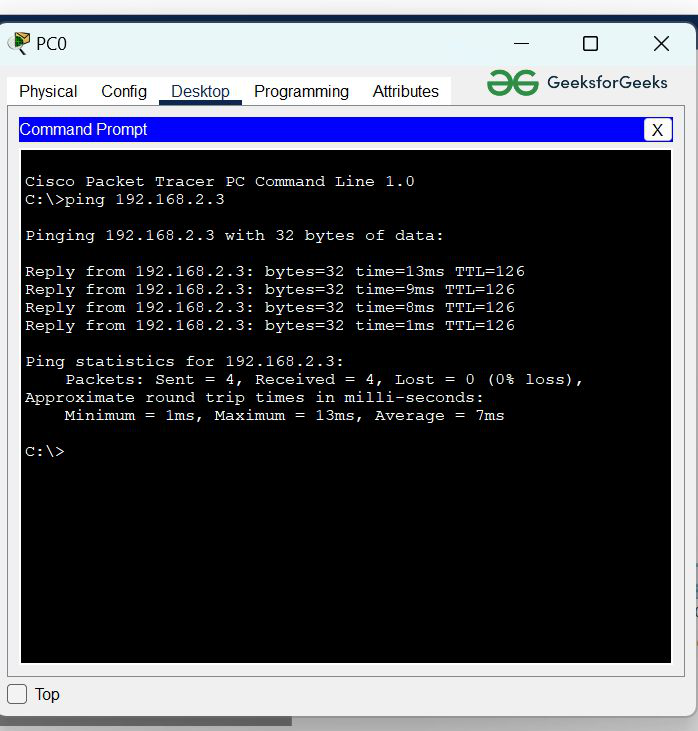
To verify the network we’ll verify the network by pinging the IP address of the target node in any Host.
- Click on PC0 then, Go to the desktop.
- Click on Command Prompt, and types this command “ping 192.168.2.3“
- In the below image we can see that we getting replies from a targeted node which means the connection is established successfully.
The below representation shows exactly how the packets are moving from the source node to the destination node.
- The PDU packet started moving from PC0 to PC3 and then came backward green tick shows that we are getting replies successfully.