Procreate is a powerful digital art application designed specifically for the iPad. It offers a range of creative features that allow you to create professional-level artwork on the go. One of the key features of Procreate is its brush engine.
Procreate’s brush engine, called Brush Studio, allows you to create and customize your own brushes. This feature allows you to create brushes that fit your style and workflow, making Procreate a powerful tool for creating professional-level artwork.
Using brushes in Procreate is easy. Simply select a brush from the brush library and start drawing or painting on the canvas. The pressure sensitivity of the Apple Pencil allows for natural-looking brush strokes and a more tactile experience. Brushes can also be resized, rotated, and adjusted for opacity and flow to achieve your desired effect.
Procreate brushes can be used to create a wide range of artwork, including illustrations, comic books, and concept art. Digital artists and designers can also benefit from using Procreate brushes to create digital mockups and designs.
We’ve curated this collection of free Procreate brush sets to help you add more detail to your digital art. The best part about these brushes is that they’re free, so you can experiment with different styles and techniques without costing you anything.
If you’re new to Procreate, you might like this collection of tutorials to help get you started.
Texture Effect Procreate Brushes
These brushes will add texture and depth to your artwork, replicating surfaces like paper, canvas, or sandpaper. They can be used to create realistic textures in digital art.
These free Procreate brushes are exactly what you think they are. They’re brushes that add graininess to your work. These speckled, dusty-looking brushes can be used to add texture or age to a project.

The Very Dry Gouache Brush lives up to its name. This brush set offers a super dry texture that makes every brush stroke visible. Plus, it will reveal different textures depending on how hard you press.

This collection includes 34 different geometry brushes. They make adding shapes, design motifs, and patterns to your work easy. They can also be used for shading.

This free cardboard Procreate brush set has a semi-streaky look that can be used for various lettering projects, from signs to business cards to logos.

Distressed Wall is a free Procreate brush set that adds a chalky-style texture to your designs. Perfect for illustration backgrounds.

Hair & Fur Procreate Brushes
These hair and fur brushes can help you create realistic textures, such as animal fur and human hair. They can give your designs and illustrations a more organic look, bringing them to life.
If you want to draw realistic hair in Procreate, this free brush set will greatly help you. With them, you can create straight or curly hair and achieve a variety of other textures.

In this collection, you will get four free Procreate brushes (including thin, harsh, ski, and ranged) that you can use to create fur or hair and also add texture to other types of art.

Stipple Effect Procreate Brushes
Stipple effect brushes add shading, depth, and intricate textures to your digital art. They are perfect for portraits, backgrounds, and creating unique effects.
This Stippling brush set contains 17 brushes, including nine stipple brushes, three liner brushes, and five textured brushes. These multi-faceted brushes can be used for just about any project you work on.

The Eclectica brush set is inspired by the retro style of the 1970s and will add a touch of pop art to your work. It is a collection of Procreate brushes you can use to create something unique. The pack includes 18 stroke and stipple brushes.

This free brush set for Procreate can be used to generate an authentic stippling effect, making it ideal for better shading.

Cloth & Textile Procreate Brushes
These cloth brushes replicate various fabrics, adding depth to your digital art by giving it a more organic look. They can be especially useful in creating clothing designs, home decor designs, and other projects that involve fabric.
This free set of Procreate brushes includes 15 swatches of varied cloth patterns that you can use to add texture to your paintings.

This free Procreate brush pack includes a natural bristle brush for creating the look of brushstrokes on a linen canvas. It also uses Procreate’s wet blending feature to imitate a realistic painting experience.

Watercolor Procreate Brushes
These brushes for Procreate offer a range of realistic watercolor textures and effects. They allow you to create beautiful, fluid strokes and blend colors seamlessly.
Here’s a collection of 48 (yes, you read that correctly) brushes for Procreate that let you replicate wet media. There are too many watercolor effects to name here, so you’ll want to download them yourself.

This Procreate brush set includes two Gouache brushes, two oil paint brushes, and two watercolor brushes. Each performs beautifully and is a solid addition to your digital art toolbox.

Painting Effect Procreate Brushes
These brushes replicate the look and feel of traditional paintbrushes. They can be used for digital painting, from realistic oil paintings to more stylized illustrations.
This Pro Painter brush set contains 31 brushes, all perfect for adding light paint or pencil textures to typography and illustrations.

Matt’s Painting Set is an all-purpose brush set for gouache artists. This free set allows you to add fine lines, texture, grit, and airbrush effects.

This collection of art brushes includes 21 different brushes for imitating real painting techniques, and they naturally have both wet and dry looks.

This free set of nine brushes will allow you to quickly paint a selection of books on a bookshelf. You can also use these brushes in Photoshop CC and Clip Studio Paint.

This free brush set will let you quickly add various types of tears to your art. You can also use these brushes as small splashes or splatters.

While milk may not be at the top of most people’s list of required brushes, this free collection will allow you to add various types of splatters, splashes, and drops to your artwork.

This collection of ten simple brushes is perfect for beginners to Procreate. These versatile brushes can be used in a multitude of ways.

This swatch collection aren’t brushes per se, but they are still incredibly useful for creating artwork in Procreate. With these, choosing colors won’t be an issue.

Nature Effect Procreate Brushes
These brushes can create various natural effects, including leaves, grass, clouds, and water. They are useful for landscape designs, botanical illustrations, and other projects that require a nature-inspired touch.
This free Procreate brush set will help speed up your landscape painting process. It includes stamps for flowers, foliage, grass, leaves, rocks, ivy, trees, and glowworms.

Here’s another set of brushes for Procreate centered around nature. This natural brush set has 20 brushes, including pencils, chalks, and shaders.

The Flora Vegetation Brushes is a massive set with a whopping 91 brushes! These brushes are designed to mimic the textures, weights, and tones of natural materials. This set is a must-have for creating nature scenes or even drawing backgrounds.

This pack of 25 free brushes allows you to add various types of textured rain to your artwork, giving it a moody, atmospheric look and feel.

The Free Floral Stamp set consists of five different brushes that help you capture the look of petals, leaves, vines, and more.

Comic & Cartoon Procreate Brushes
These brushes mimic the look and feel of traditional comic book art. They can be used to create various effects, including ink lines, halftone dots, and speech bubbles, allowing you to create unique comic and cartoon artwork.
The Comic Ink Brush Set for Procreate includes 16 inking and SFX brushes for creating comic books from scratch. From fine liners to gradients, you have everything you need here to get started.

These Procreate brushes offer brushstrokes that have become synonymous with comic books. They can be used to add the look of actual paper or brush strokes, like hash lines, to a drawing.

Here’s a collection of seven bokeh brushes for anime drawing and art. Depending on the layer style you use, you can use them in several ways to achieve different effects.

Lettering Procreate Brushes
These Procreate brushes can be used to create various lettering effects, including calligraphy, graffiti, and retro styles. You can add a personalized touch to your designs, creating custom lettering and typography for logos, titles, apparel, and other projects.
Banner Wave is a free Procreate brush set for creating textured and bold hand-drawn lettering and calligraphy.

Created for typography lovers, this free textured brush for Procreate transforms every stroke into calligraphy art. Blend tradition with modernity with this free brush set.

Unleash your inner street artist with the free graffiti brush pack for Procreate! Dive into a world of urban expression, mastering street art with brushes that capture every drip, tag, and wall wonder.

Stripe is a single brush that’s well worth downloading. It’s a smooth calligraphy or lettering brush that responds to pressure and layering—a fantastic choice for adding script typography to your work.

Designed by Kelly Sikkema, this free Procreate brush is perfect for creating beautiful typography on a dark background.

This is a nice set of lettering brushes that are a bit unusual. There’s a shrub brush, a wood grain brush, and even a worm brush!

Pencil & Pen Procreate Brushes
These pencil, pen, and ink brushes replicate the look and feel of traditional inking tools, such as brush, dip, and technical pens. They can be used for line art, illustrations, and comics.
This grain pencil and Copic marker brush set is another excellent free Procreate pack. It replicates the look and feel of real pencil strokes and lines drawn with a Copic marker.

This is a free set of pencil brushes perfect for adding texture to an item or drawing. The set includes 24 unique brushes.

Whether sketching, lettering, or embellishing intricate details, this ink brush replicates authentic ink, accommodating diverse line widths, shading, and textures. The download also includes free textured paper.

This Ballpoint Pen brush set mimics the look of a real ballpoint pen, offering fine strokes that you can layer to build shadows and contrast by applying greater pressure and using hatching.

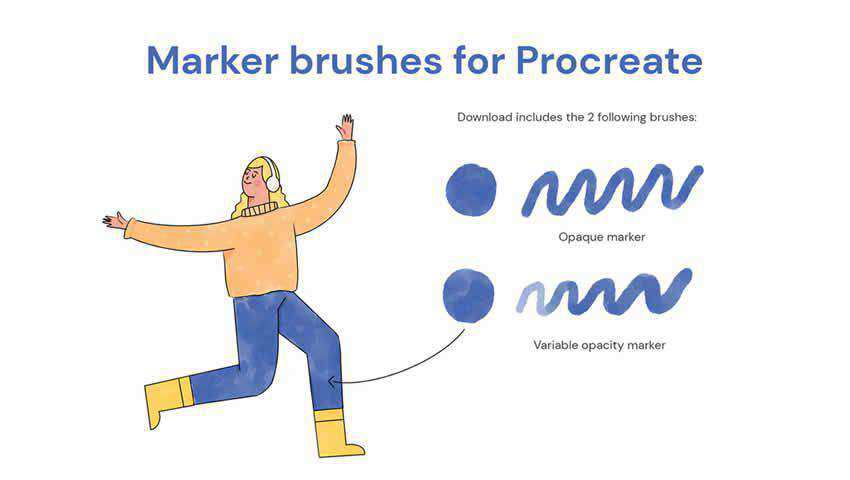
Need marker brushes? This set offers two options: an opaque marker and a variable-opacity marker. Both offer irregular coverage that looks more natural.


The Cheap Fine-Liner Brush set is a recreation of a 0.6 technical pen. It’s precise and allows you to create fine-line drawings or to fill in tiny details. It’s a great addition to any brush collection.

The Pencil, Inking, Painting Basic Brush Set consists of 7 brushes for creating comic book art from scratch. It has everything you need to conceptualize a piece from the sketch phase through painting.

Pixel Art Procreate Brushes
These Procreate brushes allow you to create authentic pixel art. You can create detailed sprites, game graphics, and nostalgic artwork.
Create your own pixel art using this free Procreate brush set. This download package includes four unique brushes, three pre-configured canvases, and a helpful user guide.

Space & Sky Procreate Brushes
These incredible brushes replicate elements of the night sky, including stars, planets, and other celestial bodies. They can be used to create various effects, including constellations, galaxies, and auroras.
This premium Procreate brush set includes 49 constellation brushes. You can download the free trial of four brushes for personal use.

With this free Procreate constellation brush set, you can add depth and create an atmosphere in your digital art. The set also includes free zodiac signs.

How to Install or Import Brushes into Procreate
Importing brushes into Procreate might vary slightly depending on your device and the method you choose. Here’s the simplest way to import brushes into Procreate:
- Download Brushes: Find and download the Procreate brush files (usually in
.brush or .brushset format) from the collection above.
- Locate the Brush Files: Once downloaded, locate the brush files on your device. You might find them in your Downloads folder or wherever you saved them.
- Transfer Files to Procreate: Upload the brush files to cloud storage services like iCloud, Dropbox, Google Drive, or others. Then, open the cloud storage app within Procreate and import the brushes. Or you can simply use AirDrop.
- Import Brushes in Procreate: Open Procreate on your device. Tap the
+ button on the top right corner of the Brush Library to open the Add panel. Choose Import to access the import options.
- Select Brush Files: Navigate to the location where you saved the brush files and select the brush files you want to import.
- Confirm Import: Procreate will display a preview of the brushes you’re about to import. Review them and tap
Import.
- Organize Brushes (Optional): After importing, you can create custom brush sets and organize your imported brushes for easier access.
- Start Using Brushes: The imported brushes will now be available in your Brush Library. Simply select a brush to start using it in your artwork.
Can You Use Photoshop Brushes in Procreate?
While using Photoshop brushes in Procreate is possible through conversion, it’s important to note that each application has its own brush engine and settings. This can lead to variations in how brushes behave and respond.
You could use a third-party tool or app to convert Photoshop .abr files to Procreate’s .brush, which Procreate can read. One tool you could use is abrMate for Windows.
To fully take advantage of Procreates’ capabilities, though, consider exploring its native brushes and using brushes that have been created specifically for the app.
Procreate Brush FAQs
-
Why Use Brush Sets in Procreate?
Brushes can dramatically change the style and feel of your artwork. They allow for more creativity and help you achieve various effects, from realistic textures to quirky patterns.
-
Are These Procreate Brush Sets Really Free?
Yes, the brushes in this collection are all free to download. Just make sure you check if there are any specific license guidelines for use.
-
Can Beginners Use These Brush Sets?
These brush sets are great for beginners because they offer many effects and styles to experiment with, making the learning process more fun.
-
Do These Brushes Work on All Versions of Procreate?
Most brushes work with different versions of Procreate, but it’s a good idea to check their compatibility with your version, especially if it’s older.
-
Can I Use These Brushes for Commercial Projects?
Most free Procreate brushes are fine for both personal and commercial projects. But it’s always a good idea to review the usage terms set by the brush creator, as some might have specific requirements or limitations.
-
Are These Procreate Brushes Customizable?
Procreate allows you to customize brushes. You can adjust settings like size, opacity, and flow to suit your requirements.
-
What Makes Procreate Brushes Different from Other Digital Art Software Brushes?
Procreate brushes are specifically designed to take advantage of Procreate’s unique features, such as Apple Pencil pressure sensitivity and tilt functionality.
Conclusion
Now that you’ve had a chance to browse this collection of free Procreate brush sets, you may have already downloaded a few or put together a nice shortlist to revisit later.
These free brushes make it easy to add precision, depth, and texture to your work without creating designs from scratch.
It’s always a good idea to read any license agreements or terms and conditions before using these Procreate brushes in your commercial work to ensure you follow the rules and do not infringe on any copyright.